CPU
Overview
- The brains of the computer
- Converts data input to information
- CPUs are measured by
–Speed – Megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz)
–Capacity or Cache: Small area on the CPU of fast memory where duplicate entries of frequently used data are stored
–Weight
Notebook CPUs are smaller and lighter weight than those made for desktops
Characteristics
- Processor speeds
- Cache
- Data bus
- Power consumption
- Word
- Cores
- Mounting
- nm process
- Chipset
- System on Chip (SOC)
Speed
How quickly instructions are processed.
- Measured in MHz or GHz
- Clock rate determines the speed of the processing capabilities
–How quickly pulses are sent to the microprocessor
–Determined within processor families
- Speeds are measured using software benchmarks
Cache
Area on the CPU of fast memory
- How do you speed up processing for frequently used data?
–Answer is cache memory: Small pools of memory that store program instructions that the CPU frequently uses.
–Available to processor as Level 1 (L1), L2, and L3 (or last) depending on manufacturer.
–Readily available by being part of the processor.
- Speed of cache is related to processor clock speed.
–L1 cache is small but fast.
–L2 cache or secondary cache is slower but still faster than conventional memory.
–L3 cache or “last” level cache is the fastest path.
Data bus
Path on which data travels
- Carries all the information to and from memory, hard disk drive, and I/O to the CPU
- Data bus interface determines how fast and path to CPU
- Interface is proprietary to the chipset manufacturer (for example: Intel or AMD)
- Examples of data bus interface types
–DMI – Direct Media Interconnect
–PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnect
–FD – Flexible Display interface
DMI 3.0, released in August 2015, allows the 8 GigaTransfers per second (GT/s) transfer rate per lane
Power consumption
Components including processor must employ low power consumption methods
- Key design consideration for notebooks especially
- Low Voltage Processors (LVP) or Ultra Low Voltage (ULV) processors conserve power and extend battery life
- Power saving utilities in Windows OS let user extend battery life
Word size
The size of the word transferred between CPU and memory
- CPU can access 32-character (bits) or 64-character (bits)
- Differentiate between 32-bit and 64-bit architecture
–32-bit can handle 32-bit words, while 64-bit processors can handle 64-bit words
–32-bit can only access 4 GB of RAM
Processor cores
Single, quad
- Heart of the CPU
–Where instructions are fetched, decoded, and processed
–Includes the Control Unit.
- Multicore processor
–Single CPU that has multiple execution cores on a single die
–Uses less power than two CPUs
Mounting the processor
Types
- Soldered on system board
- Set on socket pins
- Zero Insertion Force (ZIF)
–A mechanism to ensure the pins do not bend when the processor is set on the socket
nm process
Manufacturing process
- Refers to number of transistors on the chip
- The lower the number, the more transistors
–45 nm contains more transistors than a 65 nm processor
–The more transistors, the more instructions that can be carried out in a small space
Nanometer = 1 billionth of a meter
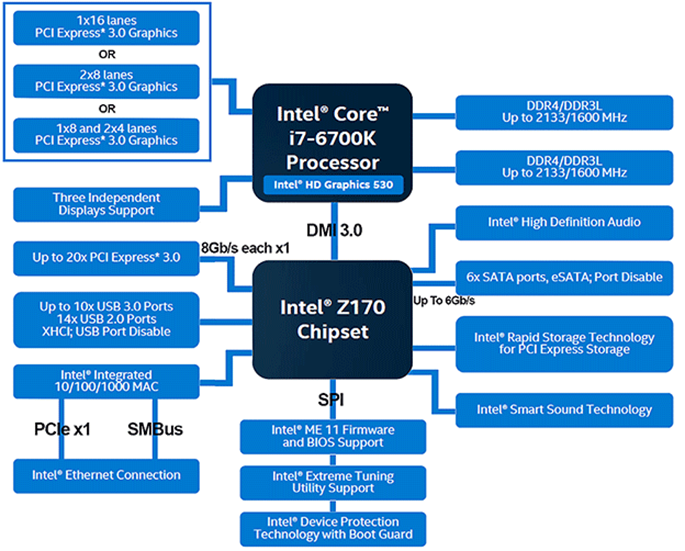
Chipset
- Notice:
–Expansion type and amount
–Displays supported
–Removable storage
–Graphics
–Network
–Storage type and amount
–Audio
–Memory type and amount

Comments